# Overview
Drupal 9 will be released on June 3, 2020 (opens new window). It is crazy to think that because it feels like Drupal 8 just came out. A lot has changed in the Drupal universe since the release of Drupal 8. Mainly the framework on which Drupal is built. No longer will it costs tens of thousands of dollars to upgrade Drupal to the next major version. This is a huge relief for many organizations that have chosen Drupal as their platform. Getting your Drupal 8 site ready for Drupal 9 is a very easy process.
Drupal 8.8 should be released on December 4, 2019. This version of Drupal 8 will contain the final deprecations for Drupal 9. With that said, this gives you a solid 6 months to get all your sites ready. So, let's dive right in and talk about deprecated code then how to test for it and fix it.
# It's All About The Deprecated Code
The main difference between Drupal 8 and 9 is deprecated code, that's it. You can search your current Drupal 8 code base for @deprecated to get a sense of what is involved. You will see examples like:
/**
* Base class for databases database tests.
*
* @deprecated in Drupal 8.4.0 and will be removed before Drupal 9.0.0. Instead
* use \Drupal\Tests\system\Functional\Database\DatabaseTestBase.
*/
abstract class DatabaseWebTestBase extends WebTestBase { }
/**
* @deprecated in Drupal 8.0.0 and will be removed before Drupal 9.0.0. Use
* \Drupal\node\Entity\Node::loadMultiple().
*
* @see https://www.drupal.org/node/2266845
*/
function node_load_multiple(array $nids = NULL, $reset = FALSE) {}
So now all we need to do is find and fix these deprecations within our Drupal 8 site and we will be good to go.
# PHPStorm
One quick and easy way to identify these deprecations is while you are writing code. If you are using the Drupal Support plugin for PHPStorm, it will mark deprecations for you like this:
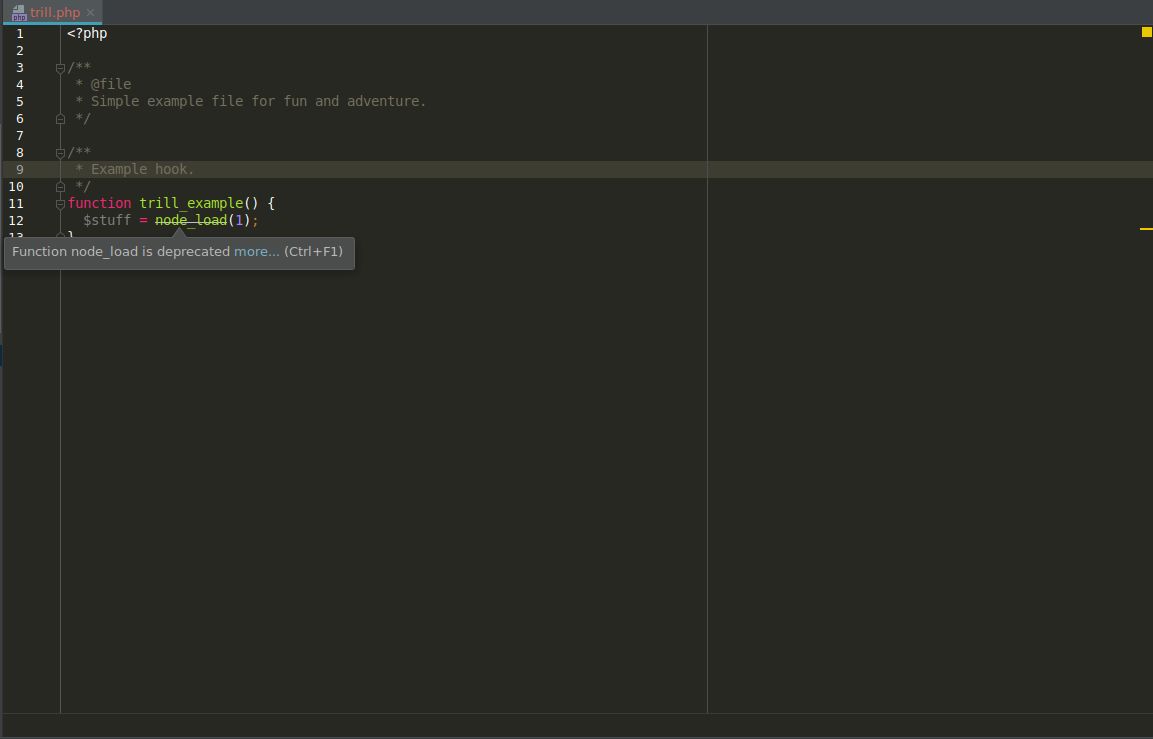
While this is great as you are writing code, it doesn't help too much to find all the deprecations in your code base. Here at Tandem, we love to automate all the things to make our lives easier. This is why we created Lando (opens new window) and we can use Lando's power to identify all our deprecations.
# Lando + PHPStan
PHPStan is a PHP Static Analysis Tool (opens new window) that can be used to identify errors within your code base via configuration files. Luckily for us Matt Glaman already created a PHPStan analysis tool for Drupal (opens new window). So all you need to do is get this composer package into your repo and then we can hook it up to Lando.
# Setting up PHPStan
So the first thing you need to do is add the required composer projects via:
composer require --dev mglaman/phpstan-drupal phpstan/phpstan-deprecation-rules
This will install the 2 packages needed to get us going. The next step is to create a PHPStan config file in the root called phpstan.neon and put this in it:
parameters:
customRulesetUsed: true
reportUnmatchedIgnoredErrors: false
# Ignore phpstan-drupal extension's rules.
ignoreErrors:
- '#\Drupal calls should be avoided in classes, use dependency injection instead#'
- '#Plugin definitions cannot be altered.#'
- '#Missing cache backend declaration for performance.#'
- '#Plugin manager has cache backend specified but does not declare cache tags.#'
includes:
- vendor/mglaman/phpstan-drupal/extension.neon
- vendor/phpstan/phpstan-deprecation-rules/rules.neon
And that is it really. PHPStan is technically setup on your local environment, now all we need to do is hook this all into Lando.
# Setting up Lando
We like to test all the things with our Lando setups, as seen in one of our Drupal 8 Starter States (opens new window). For the sake of this blog post though, we will only be using the PHPStan config. So basically all we need to do is setup Lando to call PHPStan, then have a default testing command as well for ease. Here is what a very simple .lando.yml would look like with this:
name: phpstan
recipe: drupal8
config:
webroot: web
php: 7.2
database: mariadb
services:
appserver:
build:
- "cd /app && composer install"
tooling:
phpstan:
service: appserver
cmd: /app/vendor/bin/phpstan
test:
service: appserver
description: Run Tests Locally
cmd:
- appserver: /app/vendor/bin/phpstan analyse web/modules/custom web/themes/custom
So basically this Drupal 8 Lando setup runs composer install on build, then creates 2 tooling commands: lando phpstan and lando test. The first command lando phpstan allows us to call PHPStan on whatever we want. While the second command is a default command we usually use to test all the custom development we are usually doing on the site. You can obviously tweak the paths as need be.
That is it, you are now ready to rock and roll and begin testing for all your Deprecations.
# Testing for Drupal 9 Deprecations
Lets start off by running the default lando test command on a site with no deprecations:
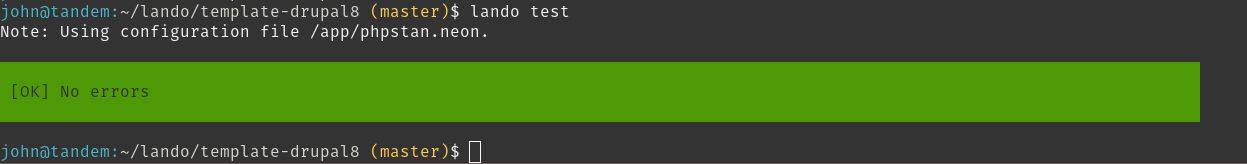
PHPStorm Lando Test Deprecations Pass
Which is great, but let's see what happens when we have a bunch of deprecations. I will be targeting specific directories using the lando phpstan command:
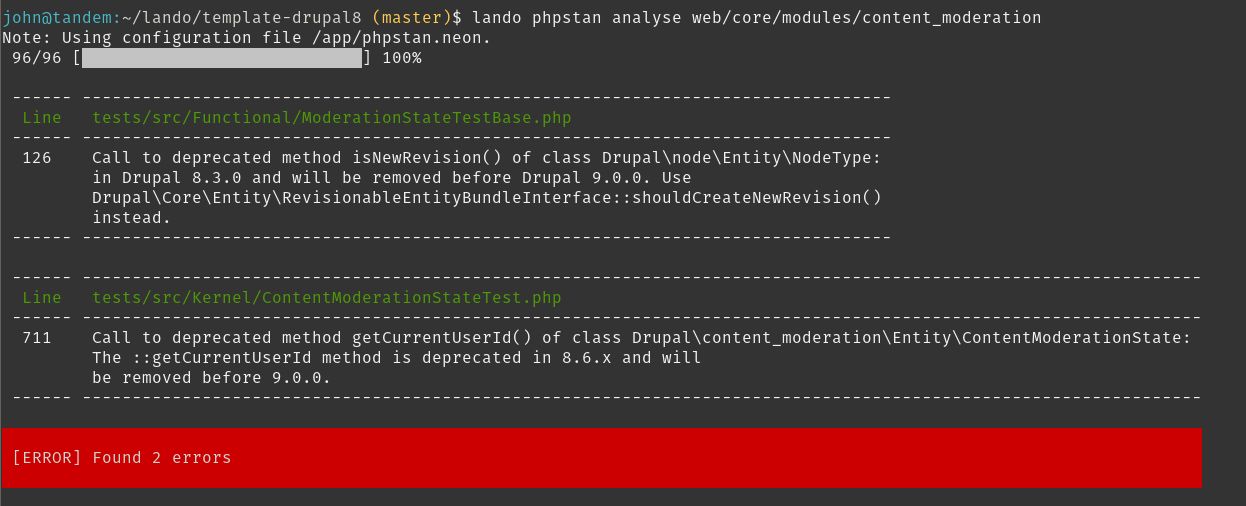
PHPStorm Lando Test Deprecations Fail
So as you can see, the core Content Moderation module has some deprecations in it still that need to be fixed. From this point you would go into the code and adjust it as need be per deprecation. This is the hardest part about this process currently. Sometimes it is a super simple fix, but every once in awhile, you may have to refactor the code a little bit. The later is very rare, but it does happen on a more complex code base.
# Automating Deprecation Testing
While I have not tried this myself yet, there is hope. Drupal 8 Rector (opens new window) looks to be promising. It doesn't seem to use PHPStan at all but uses a mix of Rector (opens new window) and PHP Coding Standards Fixer (opens new window) to get the job done. I will keep an eye on this and give this a whirl on my next Drupal 8 project and report back.
# Conclusion
Getting your code base ready for Drupal 9 is super simple with Lando + PHPStan. Within a few minutes, you can setup your local development environment to start testing away. You can easily plug this tooling into any CI testing process you may use as well.
If you need help with setting up your Drupal 9 deprecation workflow, fill out the form below and we can go from there.
